What Are The Health Benefits Of Eating Lean Meats
Introduction
Definition of Lean Meats
Lean meats are cuts of meat that have a relatively low-fat content compared to their fattier counterparts. Specifically, lean meats are defined by their limited levels of total fat, saturated fat, and cholesterol, making them a healthier option for those seeking to maintain a balanced diet.
Characteristics of Lean Meats:
- Low Total Fat Content: Lean meats contain less than 10 grams of total fat per 100 grams of cooked meat. This lower fat content helps reduce overall calorie intake while still providing essential nutrients.
- Reduced Saturated Fat: They have less than 4.5 grams of saturated fat per 100 grams. Saturated fats are known to raise cholesterol levels, so consuming lean meats helps manage heart health.
- Lower Cholesterol: Lean meats typically contain less than 95 milligrams of cholesterol per 100 grams, which is beneficial for maintaining healthy blood cholesterol levels.
Common Examples of Lean Meats:
- Poultry: Skinless chicken breast and turkey breast are prime examples of lean meats. They are highly versatile and popular in various cuisines.
- Lean Cuts of Beef: Cuts such as sirloin, tenderloin, and round steak are considered lean. These cuts are trimmed of visible fat to reduce their overall fat content.
- Pork: Pork tenderloin and pork loin chops are leaner options compared to fattier cuts like bacon or ribs.
- Fish and Seafood: Many fish, including cod, tilapia, and haddock, are naturally low in fat. Additionally, seafood like shrimp and scallops are lean protein sources.
- Game Meats: Venison and bison are naturally leaner than many traditional meats and offer a unique flavour profile.
.jpg)
Importance of Incorporating Lean Meats into a Balanced Diet
Incorporating lean meats into a balanced diet is essential for maintaining optimal health and well-being. Lean meats provide high-quality protein, essential vitamins, and minerals, all while being low in saturated fats. This combination makes them an ideal choice for those looking to achieve or maintain a healthy lifestyle. By including lean meats in your meals, you can enjoy a nutrient-dense diet that supports muscle growth, weight management, and overall health.
Nutritional Profile of Lean Meats
High-Quality Protein
Lean meats are an excellent source of high-quality protein. Protein is made up of amino acids, which are the building blocks of the body. Complete proteins contain all the essential amino acids that the body cannot produce on its own. Lean meats such as chicken breast, turkey, and lean cuts of beef and pork are complete proteins, providing all the necessary amino acids for various bodily functions.
Role of Protein in Muscle Growth and Repair
Protein plays a crucial role in muscle growth and repair. It helps to rebuild and strengthen muscle tissues after physical activity, making it particularly important for athletes and individuals who engage in regular exercise. Consuming adequate amounts of protein from lean meats supports muscle maintenance and development, enhancing overall physical performance and recovery.
Low in Saturated Fats
Lean meats are characterised by their low saturated fat content. Unlike fattier cuts of meat, lean meats have less than 4.5 grams of saturated fat per 100 grams. This significant reduction in saturated fats makes lean meats a healthier option, as high saturated fat intake is associated with increased levels of LDL cholesterol, which can contribute to heart disease.
Comparison with Fatty Cuts of Meat
Fatty cuts of meat, such as ribeye steak or pork belly, contain higher levels of saturated fat. In contrast, lean cuts like chicken breast, turkey breast, and pork tenderloin have significantly lower saturated fat content, making them a better choice for maintaining a healthy heart.
Benefits of Lower Saturated Fat Intake
Reducing saturated fat intake by choosing lean meats can help lower LDL cholesterol levels, decrease the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases, and promote overall heart health. This makes lean meats an important component of a heart-healthy diet.
Rich in Essential Nutrients
Lean meats are rich in essential vitamins and minerals, including B vitamins, iron, and zinc. These nutrients are vital for various bodily functions and overall health.
Overview of Vitamins and Minerals (B Vitamins, Iron, Zinc)
- B Vitamins: Lean meats are a good source of B vitamins, particularly B12, which is crucial for energy metabolism and the formation of red blood cells.
- Iron: Iron from meat, known as heme iron, is easily absorbed by the body and is essential for transporting oxygen in the blood.
- Zinc: Zinc supports immune function, protein synthesis, and DNA production.
Importance of These Nutrients for Overall Health
These essential nutrients play critical roles in maintaining energy levels, supporting the immune system, and promoting overall physical health. Including lean meats in your diet ensures you receive these vital nutrients in adequate amounts.
Health Benefits
Weight Management
Lean meats are beneficial for weight management due to their high protein content and low-calorie density.
Lean Meats as Part of a Calorie-Controlled Diet
Including lean meats in a calorie-controlled diet can help with weight loss or maintenance. The high protein content helps you feel full for longer, reducing overall calorie intake.
Satiety and Appetite Control
Protein-rich foods like lean meats promote satiety and help control appetite, making it easier to stick to a healthy eating plan and avoid overeating.
Heart Health
Choosing lean meats over fatty cuts can have a positive impact on heart health.
Reduced Risk of Cardiovascular Diseases
Consuming lean meats helps reduce the intake of saturated fats, which in turn lowers the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
Impact on Cholesterol Levels
Lean meats contribute to lower LDL cholesterol levels, promoting better heart health and reducing the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
Muscle Growth and Maintenance
Lean meats are essential for muscle growth and maintenance, especially for athletes and older adults.
Importance for Athletes and Active Individuals
For athletes and active individuals, the high-quality protein in lean meats supports muscle recovery and growth, enhancing physical performance.
Role in Preventing Muscle Loss in Older Adults
As we age, muscle mass naturally decreases. Consuming adequate protein from lean meats helps prevent muscle loss, maintaining strength and mobility in older adults.
Blood Sugar Regulation
Lean meats can play a role in regulating blood sugar levels.
Impact on Insulin Sensitivity
High-protein diets that include lean meats have been shown to improve insulin sensitivity, helping to regulate blood sugar levels.
Benefits for Individuals with Diabetes
For individuals with diabetes, incorporating lean meats into their diet can help manage blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of complications associated with the disease.
Specific Types of Lean Meats and Their Benefits
Chicken Breast
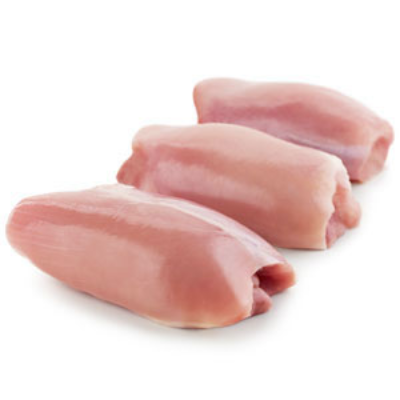

Nutritional Profile: Chicken breast is one of the leanest sources of protein available, with approximately 31 grams of protein and only 3.6 grams of fat per 100 grams. It is also a good source of B vitamins, phosphorus, and selenium.
Popularity and Versatility in Recipes: Chicken breast is incredibly popular due to its versatility in cooking. It can be grilled, baked, poached, or stir-fried, and it adapts well to a wide range of flavours and cuisines. Its mild taste makes it a favourite ingredient in numerous dishes, from salads and sandwiches to stir-fries and casseroles.
Turkey

Benefits Compared to Other Poultry: Turkey, particularly the breast, is another excellent source of lean protein, offering similar nutritional benefits to chicken but with slightly fewer calories. It is rich in B vitamins, selenium, and zinc.
Seasonal and Everyday Uses: While turkey is often associated with festive meals like Christmas, it is also a great everyday protein source. Ground turkey can be used in place of beef in many recipes, and turkey breast can be roasted or grilled for a healthy meal option.
Pork Tenderloin

Lean Alternative to Other Pork Cuts: Pork tenderloin is a lean cut of pork that contains about 23 grams of protein and only 3.5 grams of fat per 100 grams, making it a healthier choice compared to fattier cuts like pork belly or ribs.
Nutritional Advantages: In addition to being low in fat, pork tenderloin is rich in thiamine, niacin, and vitamin B6, which are essential for energy metabolism and overall health.
Lean Beef Cuts (e.g., Sirloin, Tenderloin)
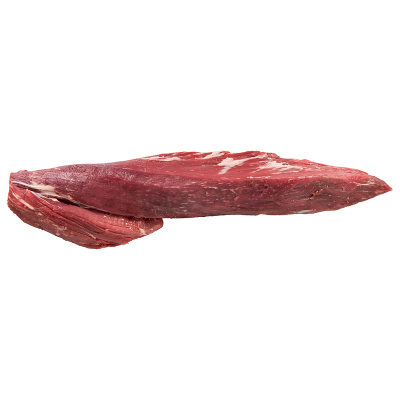

Comparison with Fattier Cuts: Lean beef cuts such as sirloin and tenderloin have significantly less fat than cuts like ribeye or T-bone. For instance, sirloin contains about 25 grams of protein and 6 grams of fat per 100 grams, whereas ribeye can have more than twice the fat content.
Best Cooking Methods to Retain Leanness: To retain their leanness, these cuts should be cooked using healthy methods such as grilling, broiling, or roasting. Avoid frying or adding excessive oils and butter.
Fish and Seafood
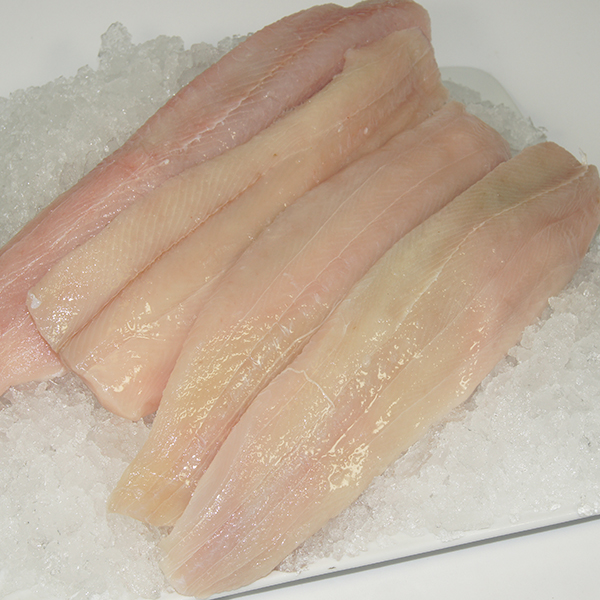

Lean Fish Options (e.g., Cod, Tilapia): Lean fish like cod and tilapia are excellent low-fat protein sources. They provide around 20 grams of protein and only 1 gram of fat per 100 grams. They are also low in calories and rich in essential nutrients.
Additional Benefits of Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Fish and seafood, particularly oily fish like salmon and mackerel, offer the added benefit of omega-3 fatty acids, which are crucial for heart health, brain function, and reducing inflammation.
Practical Tips for Incorporating Lean Meats into Your Diet
Cooking Methods
Healthy Cooking Techniques (Grilling, Baking, Steaming): Opt for grilling, baking, or steaming lean meats to maintain their nutritional benefits without adding unnecessary fats. These methods help retain moisture and enhance the natural flavours of the meat.
Avoiding Added Fats During Preparation: Avoid using excessive oils, butter, or high-fat sauces when preparing lean meats. Instead, use non-stick cooking sprays, marinades, and broths for added flavour without the extra calories.
Meal Planning
Tips for Balanced Meals: Create balanced meals by pairing lean meats with a variety of vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats. This ensures you get a wide range of nutrients while maintaining a healthy diet.
Incorporating Lean Meats into Various Recipes: Incorporate lean meats into soups, salads, stir-fries, and casseroles. Experiment with different spices, herbs, and marinades to keep meals interesting and flavourful.
Portion Control
Recommended Serving Sizes: Stick to recommended serving sizes, which are generally around 85-115 grams (3-4 ounces) of cooked lean meat per meal. This helps control calorie intake and ensures a balanced diet.
Balancing with Other Food Groups: Balance your meals by including appropriate portions of vegetables, fruits, whole grains, and healthy fats alongside lean meats. This promotes overall nutritional balance and well-being.
Common Myths and Misconceptions
Myth: Lean Meats Are Less Flavourful
Tips for Enhancing Flavour Without Adding Fat: Enhance the flavour of lean meats without adding fat by using herbs, spices, and citrus juices. Marinades made with ingredients like garlic, ginger, lemon, and herbs can add depth and complexity to the taste.
Use of Herbs, Spices, and Marinades: Experiment with different combinations of herbs and spices to find your favourite flavours. Marinades can also help tenderise the meat and infuse it with additional taste.
Myth: All Red Meat Is Bad for You
Differentiating Between Lean and Fatty Cuts: Not all red meat is created equal. Lean cuts like sirloin, tenderloin, and flank steak are lower in fat and can be part of a healthy diet when consumed in moderation.
Moderation and Balance in a Healthy Diet: Include lean red meat in moderation, balancing it with other protein sources like poultry, fish, and plant-based options. This ensures a varied and balanced diet.
Conclusion
Summary of Health Benefits
Lean meats provide high-quality protein, and essential nutrients, and are low in saturated fats. They support muscle growth, weight management, heart health, and blood sugar regulation.
Encouragement to Include Lean Meats in Your Diet
Incorporate lean meats into your diet to enjoy these health benefits. Experiment with different cuts and recipes to find what works best for you. Lean meats can be a delicious and nutritious part of a balanced, healthy lifestyle.
 © 2016 University Meat |
© 2016 University Meat |